theHarvester Custom Modules: LinkedIn Enumeration and Breach Correlation
theHarvester custom modules enable specialized OSINT collection through LinkedIn enumeration and breach data correlation, providing comprehensive intelligence gathering capabilities for security research.
TheHarvester systematically vacuums corporate intelligence from public data streams that organizations leak without realizing it. Written by Christian Martorella at Edge-Security, this Python framework aggregates data from 43 sources into consolidated intelligence reports. Version 4.8.2 delivers everything from basic email enumeration to sophisticated organizational mapping through Certificate Transparency logs, breach databases, and social media scraping.
Corporations dump massive amounts of operational data through public channels daily. Employee LinkedIn profiles reveal organizational structure. GitHub repositories expose internal naming conventions. SSL certificates broadcast subdomain architectures. TheHarvester systematically collects this scattered intelligence and presents it as actionable reconnaissance data.
Plugin Architecture
TheHarvester's power comes from its plugin-based architecture. Each intelligence source operates as an independent module implementing standardized collection interfaces. Adding new sources requires minimal code changes because the framework abstracts away networking complexity, rate limiting, and output standardization.
Data source modules handle everything from certificate transparency scraping to breach database queries through consistent APIs. The core framework provides proxy rotation, user agent randomization, and detection evasion while modules focus on source-specific collection logic. This separation enables rapid integration of new intelligence feeds without touching core framework code.
Result standardization ensures every piece of collected data includes confidence scoring, source attribution, timestamps, and quality indicators. Whether pulling emails from Hunter.io or subdomains from Certificate Transparency logs, output follows identical formatting that enables automated correlation across intelligence streams.
Framework services abstract common reconnaissance challenges. Rate limiting prevents source detection. Proxy rotation maintains anonymity across extended operations. User agent randomization mimics legitimate browsing patterns. Output standardization enables automated analysis pipelines to process results from any supported source.
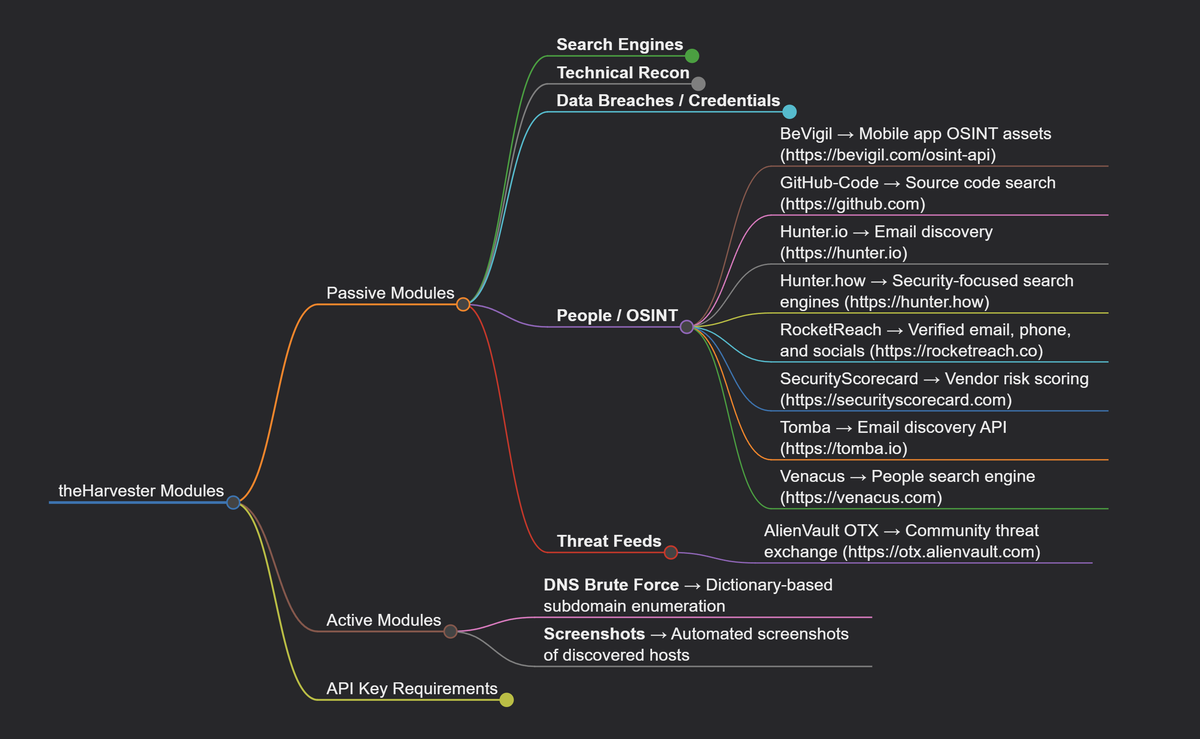
43 Data Streams for Organizational Mapping
TheHarvester taps 43 distinct intelligence sources ranging from search engines to specialized security databases. Free sources include DuckDuckGo, Certificate Transparency logs, DNS enumeration services, and GitHub code searches. Premium sources require API keys but provide higher-quality intelligence.

High-value API sources include Shodan for internet-connected device discovery, SecurityTrails for historical DNS data, Hunter.io for email enumeration, and Censys for certificate analysis. Each source provides unique intelligence perspectives that complement others in comprehensive reconnaissance operations.
Source Selection Strategy: Certificate Transparency logs provide subdomain enumeration that cannot be blocked or rate-limited. Breach databases reveal credential exposure patterns. Professional networks expose organizational hierarchies. Search engines surface publicly indexed sensitive information. Combining multiple source types creates comprehensive organizational profiles.
API rate limiting varies dramatically across sources. Hunter.io restricts free accounts to 10 queries monthly. Bevigil allows 50 free searches. Premium sources like SecurityTrails offer thousands of queries but require subscription fees. Effective reconnaissance requires understanding these limitations and planning collection accordingly.
Operational Intelligence Collection
Basic reconnaissance follows predictable execution patterns but delivers comprehensive results when properly configured.
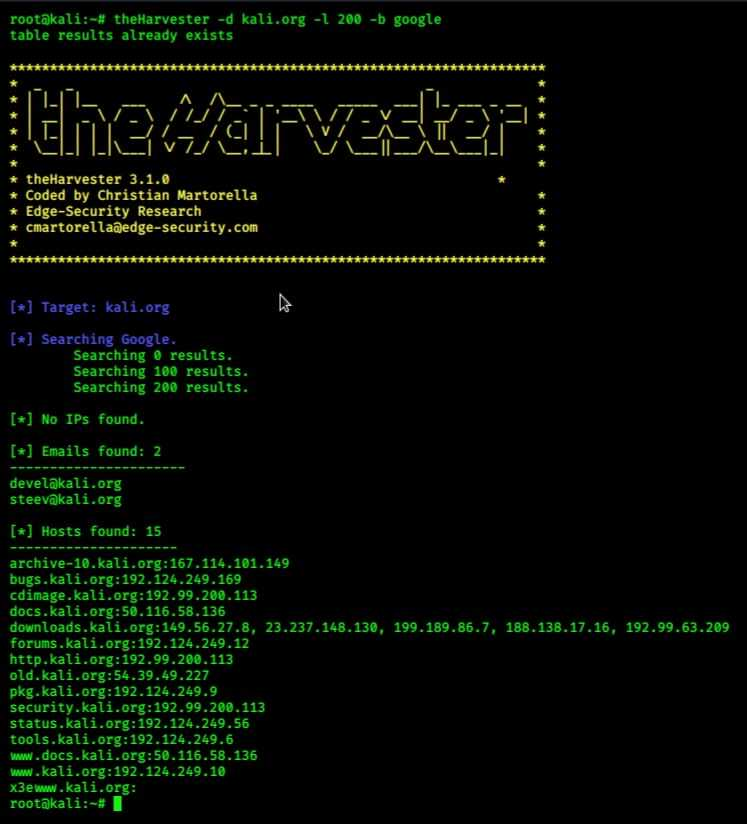
Single-source enumeration tests specific intelligence feeds: theHarvester -d target.com -l 100 -b shodan pulls device information from Shodan's internet scanning database. Multi-source collection aggregates intelligence across all available feeds: theHarvester -d target.com -l 50 -b all -f results.html generates comprehensive organizational profiles.
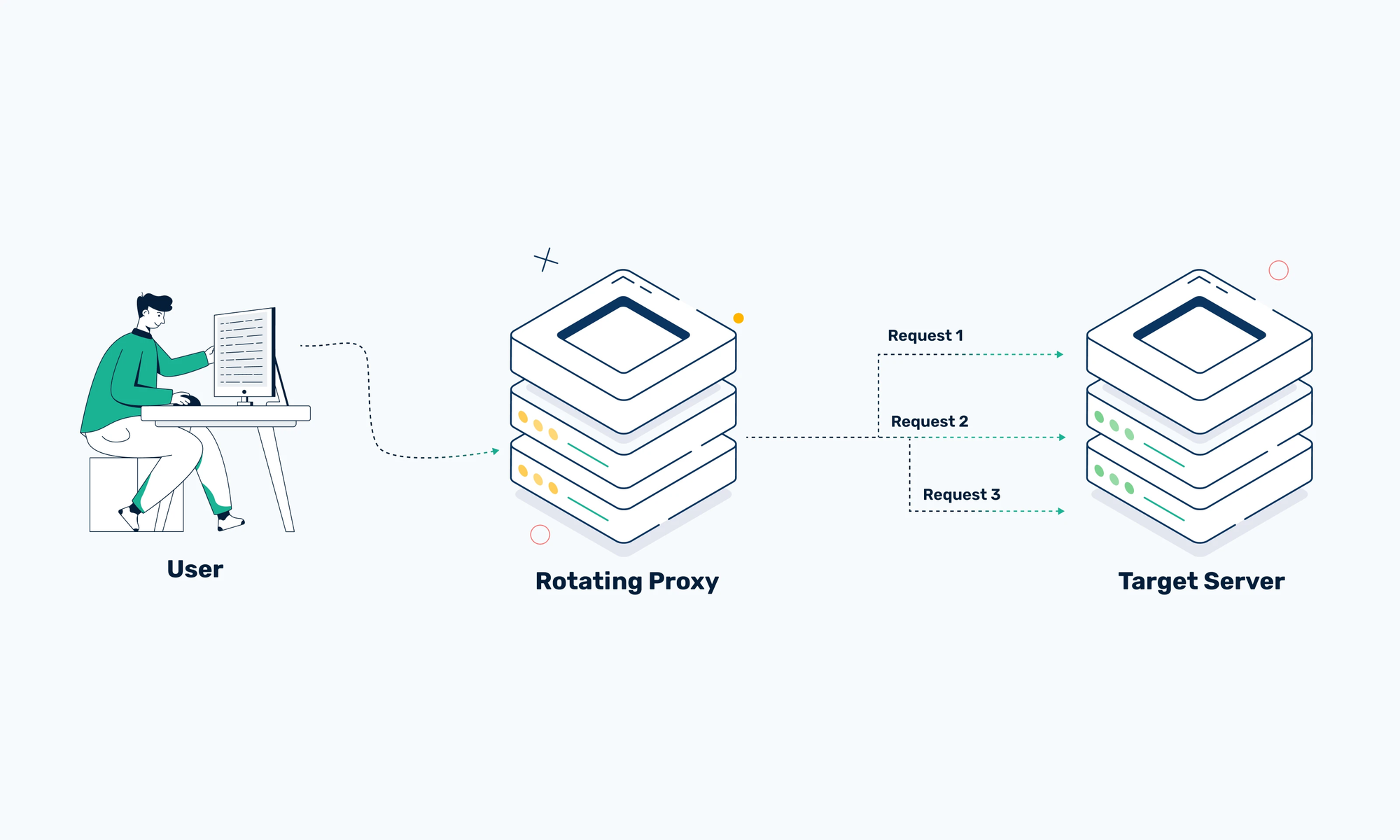
Detection Evasion becomes critical during extended operations. Most sources implement anti-automation measures that detect rapid sequential queries. LinkedIn blocks repeat searches almost immediately. Google implements sophisticated pattern detection. Certificate Transparency logs remain immune to blocking because they operate as public audit mechanisms.
Proxy rotation through proxies.yaml configuration maintains anonymity across long collection sessions. User agent randomization occurs automatically but aggressive querying still triggers defensive responses from most commercial sources.
Real-World Collection Example: Reconnaissance against technology company "TechCorp" with domain techcorp.com typically yields 30-50 unique email addresses revealing organizational structure, 15-25 subdomains exposing internal services like VPN endpoints and staging environments, 5-10 IP addresses for infrastructure mapping, and employee names from LinkedIn integration for social engineering preparation.
Breach Data Integration and Intelligence Enhancement
TheHarvester integrates with breach databases like HaveIBeenPwned and Dehashed to correlate collected email addresses against known credential exposures. This correlation identifies potential attack vectors and assesses organizational security exposure through publicly documented breaches.

Cross-reference analysis combines social media profiles, professional networks, and breach data to build comprehensive targeting profiles. Timeline correlation reveals hiring patterns, infrastructure changes, and organizational evolution through systematic analysis of collected intelligence timestamps.
Pattern recognition across large datasets identifies anomalies that manual investigation would miss. Unusual subdomain naming patterns might indicate hidden services. Inconsistent organizational information could suggest deception operations or compromised infrastructure. Statistical analysis reveals relationships between collected data points that inform subsequent reconnaissance targeting.
Attribution Analysis correlates collected intelligence with known threat actor techniques and infrastructure patterns. This analysis assesses potential organizational threats based on publicly available information and historical attack patterns.
Module Development: Custom Intelligence Sources
TheHarvester's modular architecture enables rapid development of custom collection capabilities. Each module implements standardized interfaces for initialization, search execution, and result extraction.
class CustomSource:
def __init__(self, word, limit):
self.word = word
self.limit = limit
self.results = []
def do_search(self):
# Source-specific collection logic
pass
def get_emails(self):
return self.emails
def get_hostnames(self):
return self.hostnamesRate limiting implementation within modules prevents source detection while maximizing collection efficiency. Sophisticated modules implement randomized delays and behavioral mimicry to avoid triggering automated defenses. Data validation ensures collected information accuracy through cross-referencing and consistency checking.
Custom modules can target specialized intelligence sources like internal corporate directories, specialized search engines, or proprietary databases. The standardized interface ensures custom modules integrate seamlessly with existing framework services and analysis pipelines.
Advanced Analysis and Multi-Source Correlation
Raw theHarvester output requires analysis and correlation to produce actionable intelligence. Automated analysis pipelines process collected data through machine learning classification, statistical analysis, and expert system reasoning to identify significant relationships and potential security implications.
Multi-source intelligence fusion combines theHarvester results with threat intelligence feeds, vulnerability assessments, and organizational security data. This integration provides comprehensive threat analysis supporting security operations and risk assessment activities.
Intelligence Workflows transform raw reconnaissance data into structured intelligence products. Executive summaries highlight key findings and risk assessments. Technical reports provide detailed analysis supporting security operations. Tactical intelligence supports immediate security decision-making.
Quality assurance validates collection accuracy and analysis reliability through automated verification, source cross-referencing, and confidence scoring. Feedback mechanisms continuously improve intelligence production capabilities and analytical accuracy.
Operational Security
Organizations face systematic intelligence collection from adversaries using identical tools and techniques. Defensive strategies must assume persistent reconnaissance and implement appropriate countermeasures without relying on security through obscurity.
Information exposure reduction limits reconnaissance attack surfaces through email obfuscation, subdomain access controls, and careful management of public information disclosure. Collection detection monitors for systematic reconnaissance through behavioral analytics and threat intelligence correlation.
Counter-intelligence operations can provide false information to automated collection systems, degrading adversary intelligence confidence and creating analytical uncertainty. Security awareness training addresses information disclosure through professional networks and social media that creates collection opportunities.
Reconnaissance Detection identifies systematic collection attempts through log analysis and behavioral pattern recognition. Multiple automated queries from single sources, unusual access patterns, and correlation with known reconnaissance tools can indicate active intelligence collection operations.
Integration
TheHarvester functions as initial collection within comprehensive intelligence workflows. Raw data requires correlation with additional sources to produce actionable security intelligence supporting operational decision-making.
Intelligence fusion combines theHarvester reconnaissance with technical vulnerability assessments, threat actor profiling, and organizational security evaluations. This multi-source approach provides comprehensive threat analysis that informs security strategy and tactical operations.
Reporting formats serve different organizational needs while maintaining operational security. Executive briefings highlight strategic implications. Technical analysis supports security team operations. Tactical intelligence enables immediate security response activities.
Automated Integration processes theHarvester output through intelligence analysis platforms that correlate reconnaissance data with threat indicators, vulnerability information, and security event data. This automation enables real-time threat assessment and rapid security response.
Key Resources:




