Monero 0.18.4.5 Fixes Ledger Crash Bug
Monero 0.18.4.5 arrives with Ledger Nano Gen5 compatibility and patches for daemon synchronization problems.

Monero pushed version 0.18.4.5 on January 11, 2026, a maintenance release codenamed "Fluorine Fermi" that targets hardware wallet compatibility and daemon stability. If you run Monero with a Ledger device, this update matters.
The primary fix addresses a bug crashing the Ledger Monero app during transaction signing. Hardware wallet users encountered frozen screens and failed transactions when attempting to move funds. The crash stemmed from communication issues between the Monero wallet software and Ledger firmware, leaving users unable to access their XMR without switching to software-only wallets or waiting for a patch.

This release also brings Ledger Nano Gen5 support to Monero. The newest hardware wallet line launched with broader cryptocurrency compatibility, but Monero support required explicit development work given the coin's unique cryptographic requirements. Ring signatures, stealth addresses, and RingCT demand more complex transaction construction than transparent blockchains, which means hardware wallet integration takes longer and breaks more easily.
Beyond Ledger fixes, the developers patched a daemon race condition causing connection drops during blockchain synchronization. Nodes downloading or verifying the chain would occasionally lose peer connections mid-sync, forcing restarts and extending initial sync times. The fix stabilizes peer connections during high-throughput synchronization phases.
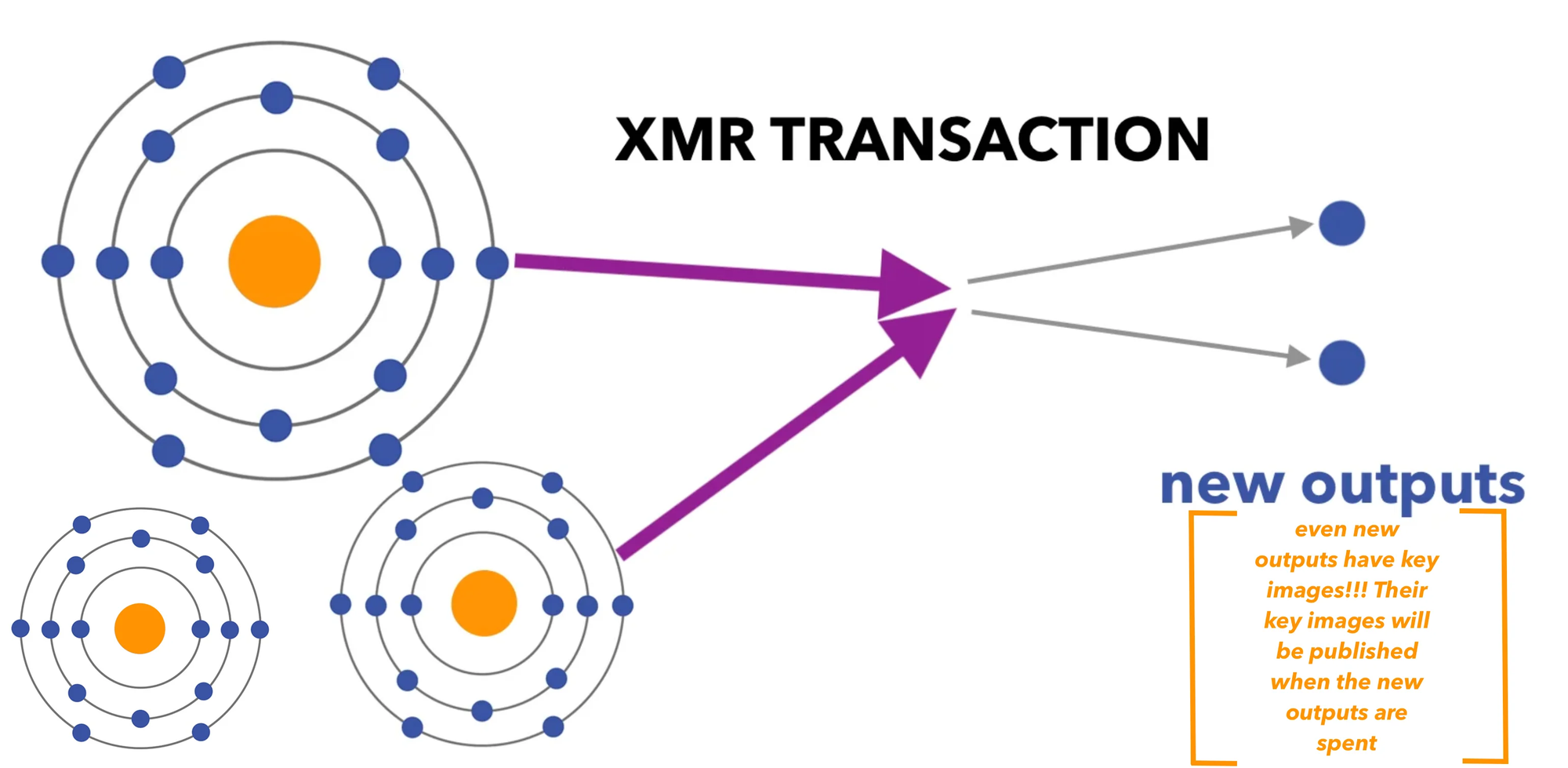
A wallet-level edge case affecting key image spend status tracking also got corrected. Key images prevent double-spending in Monero's privacy model by creating a unique cryptographic fingerprint for each spend without revealing which output was actually spent. The edge case caused incorrect spend status reporting in certain wallet configurations, potentially confusing users about their available balance.
Terminal color detection improvements round out the technical changes, helping the command-line interface display correctly across different terminal emulators and configurations.
The development stats reflect a targeted maintenance effort: seven contributors pushed 16 commits adding 76 new lines of code. Contributors tobtoht, plowsof, nahuhh, selsta, laanwj, iamamyth, and j-berman all contributed to the release. The compact changeset indicates focused bug fixing rather than feature expansion, which aligns with the "maintenance release" designation.
Binary downloads cover Windows 32-bit and 64-bit, macOS for Intel and Apple Silicon, Linux across x64, armv7, armv8, and riscv64 architectures, multiple Android variants, and FreeBSD. The project maintains broad platform support because privacy tools need to run wherever users operate.
Verification remains critical when downloading cryptocurrency software. The Monero project provides SHA256 hashes for all binaries and publishes a GPG-signed hash list. Verification keys live in the source repository under /utils/gpg_keys. Two verification guides exist for different user experience levels, one streamlined and one detailed.
Verifying downloads protects against supply chain attacks where malicious actors replace legitimate software with compromised versions. A wallet binary modified to leak private keys or redirect funds would devastate users who skip verification. The few minutes spent checking hashes and signatures eliminates entire categories of attack vectors.
Hardware wallet integration matters for Monero users because it moves private key operations off internet-connected computers. Even if your desktop gets compromised by malware, hardware wallet architecture keeps signing keys isolated on the secure element, though supply chain attacks and firmware vulnerabilities remain possible attack vectors. The tradeoff involves added complexity and occasional compatibility breaks like the bug this release fixes.
Monero occupies a specific position in cryptocurrency. The protocol enforces privacy by default through ring signatures hiding the true sender among decoys, stealth addresses generating unique receiving addresses per transaction, and RingCT concealing transaction amounts. Every transaction benefits from these protections at the protocol level, removing the "optional privacy" problem where privacy features become suspicious by association. Network-level metadata and timing analysis fall outside the protocol's guarantees.
This architectural commitment to privacy requires more development resources for features that other cryptocurrencies implement trivially. Hardware wallet support, light wallet infrastructure, and exchange integrations all demand extra engineering work to maintain privacy guarantees while providing functionality users expect. The 0.18.4.5 release represents ongoing maintenance keeping that infrastructure functional.
Users running Ledger hardware wallets should upgrade immediately to restore transaction signing capability. Everyone else benefits from the daemon stability improvements and should update at their normal maintenance pace. The release carries no consensus changes requiring urgent network-wide adoption, so timing remains flexible for users without hardware wallet issues.
Download from getmonero.org/downloads, verify the binary hashes against the signed hash list, and follow the verification guides if the process is unfamiliar. The full changelog comparing v0.18.4.4 to v0.18.4.5 lives on GitHub for those wanting implementation details.